Introduction:
Many savvy investors choose real estate to develop wealth because of its ability to earn a steady income, track record of long-term growth, and capacity to diversify an investment portfolio. In reality, people who diversify a portion of their portfolio into real estate investments outperform those who do not.
Why should you invest in real estate?
Many savvy investors choose real estate to develop wealth because of its ability to earn a steady income, track record of long-term growth, and capacity to diversify an investment portfolio.
In reality, people who diversify a portion of their portfolio into real estate investments beat those who do not.
Advantages of real estate investing.
Real estate has numerous advantages. With well-chosen properties, investors can experience continuous cash flow, attractive yields, tax advantages, and diversification—and it is possible to use real estate to build wealth.
Are you thinking about investing in real estate? Here’s all you need to grasp about real estate benefits and why they’re such a fantastic investment.
Real estate offers a distinct blend of short- and long-term profit potential and diversification power not seen in other asset types. Check these out.
Real estate investors benefit from various tax benefits and deductions, resulting in tax savings. You can generally deduct appropriate property ownership, operation, and management costs.
One appealing aspect of real estate investing is generating stable cash flow. Two examples are equity ownership in apartment buildings that create money through rental payments or loans that generate income through interest payments.
While smaller equity investments like homes can be purchased directly, other investment vehicles, such as funds, provide access to more considerable income-producing assets to investors of all sizes.
As you pay your mortgage, you can build equity, which adds to your net worth. As your equity grows, you’ll have more leverage to purchase additional properties, increasing your income flow and wealth even further.
Competitive Risk-Adjusted Returns
Real estate returns vary according to geography, asset class, and management. Still, many investors strive to outperform the S&P 500’s average returns—what many people refer to as “the market.”
Equity ownership has the rare ability to generate both cash flow and long-term appreciation. Both residential and commercial real estate have long-term growth records that may complement a portfolio.
The market value of residential real estate in the United States climbed by 36% between 2008 and 2018 and 173% between 1998 and 2018.
Diversification
Private real estate, as an asset class with a low correlation to the stock market, provides significant diversification. An investor decreases exposure to needless risk of loss by diversifying an investment portfolio among and across uncorrelated asset classes, such as private real estate, which helps to produce a more stable and lucrative portfolio.
The 20% Rule of Real Estate has a higher return potential with lesser volatility.
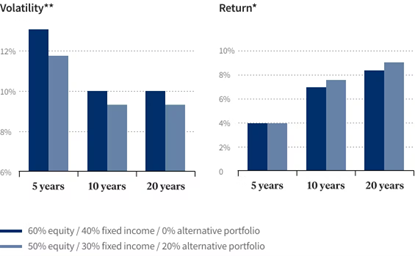
**Hypothetical portfolios comprised of the S&P 500 (stock) and the Barclays Capital US Aggregate Bond (fixed income)
*Hypothetical portfolios consist of the S&P 500 (stock), the Barclays Capital US Aggregate Bond (fixed income), and an equally weighted blend of alternatives consisting of the HFRI Fund Weighted Composite (hedge funds). Cambridge U.S. Private Equity and Barclays CTA (managed futures) (private equity). Past success does not guarantee future results.
Source: Baird Private Wealth Management, The Role of Alternative Investments in a Diversified Investment Portfolio.
What benefits does real estate provide that stocks and bonds do not?
Real estate investments often supplement portfolios highly weighted toward stocks and bonds, as their unique qualities can provide benefits not available in the stock market.
Less volatility, more consistency
Because they are exchanged in distinct marketplaces, private market real estate has no association with stock market performance. This divergence, combined with the less efficient dynamics of the private market and significantly fewer large daily fluctuations in prices, has resulted in far less volatile and more steady performance than the stock market.
The actual return on equity and housing trends
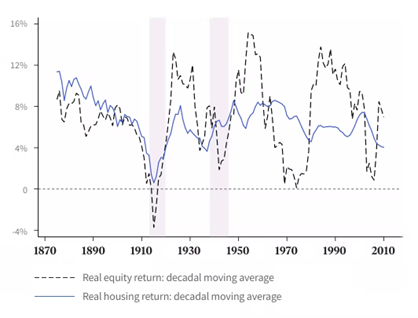
Note: Mean returns are weighted by real GDP for 16 nations, moving averages over a decade. The source is The Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, published The Rate of Return on Everything, 1870-2015.
In comparison, the publicly traded stocks in the United States are decreasing, and correlation is increasing, leading to increased volatility. Between 1950 and 1999, the S&P 500 experienced 81 daily movements of 3% or more. Between 2000 and 2019, the S&P 500 experienced 120 daily moves of 3% or more.
Real estate can hedge inflation. Land has an intrinsic worth since it is naturally restricted in supply. Land’s value rises as it gets scarcer, especially in high-demand locations.
Residential land values in the United States climbed by 31% between 2008 and 2018 and 169% between 1998 and 2018. Real estate is a distinctive hard asset since rising demand can boost its worth and rental price potential.
Real estate may defend against inflation in a variety of ways:
- Property values may rise faster than inflation, resulting in capital gains.
- Investment property rents might increase to keep up with inflation.
- Houses funded with a fixed-rate loan will diminish the approximate monthly mortgage payments over time.
For example, $1,000 a month as a fixed payment will become less problematic as inflation erodes that $1,000’s purchasing power.
How do real estate investments generate revenue?
When it comes to generating money through real estate investing, there are just a few options. Though the concepts are simple to grasp, don’t be misled into thinking they are simple to apply and execute.
Understanding the fundamentals of real estate can help investors optimize their profits. When done appropriately, real estate provides investors with another asset class, boosts diversity, and can decrease risks.
Real estate can generate income and appreciation in the short and long term.
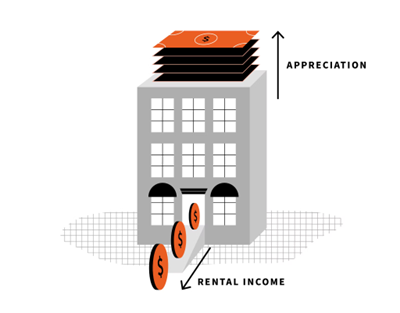
Income
Debt investments like a mortgage can yield interest at a fixed rate of return. Loans are frequently less risky than stock investments, making them appealing to people looking for income.
Rental payments from equity assets can provide revenue. Real estate investors with equity ownership can produce significant income over time as a long-term investment, depending on market demand and occupation.
Appreciation
While an investment property earns money from paying tenants, the property itself can appreciate. When the property is sold, equity investors may receive a lump sum payout and any income produced throughout the investment’s lifespan.
What are the tax benefits of real estate investing?
Real estate investments can provide valuable tax benefits, but, as with most investments, tax ramifications depend on various circumstances, including the investment vehicle.
Several factors influence taxation amounts and timing for each investor, including the amount and type of return produced, investment duration, investment vehicle, and other factors. As a result, it is essential to consult your tax expert regarding taxes for your assets.

Most importantly, any income and capital gains derived through appreciation will be taxed. As of 2018, profits generated and redistributed by REITs and real estate mutual funds can be eligible for a 20% tax deduction. These investment vehicles’ pass-through form allows their investors to seek this deduction on qualifying business income under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
What is the average lifespan of a real estate investment?
Real estate has a maximum earning potentially available over several years.
- 7.6 years – The average length of time institutional investors keep commercial real estate
- 5 years – We advise five years as a holding duration for investors.
Real estate, particularly in the private market, is an illiquid investment. This characteristic means that properties sell slowly, but it can also reduce asset volatility with increased liquidity, such as publicly-traded equities and bonds.
Real estate typically has a holding term or time horizon of several years. Institutional investors hold commercial real estate for an average of 7.6 years, although direct investors who own residential investment properties may keep them for far longer.
What are my real estate investment options?
Two investment options are active (hands-on) and passive (hands-off). Each method has advantages and cons.
The direct ownership of an asset is referred to as active real estate. This method allows investors more control but also more accountability and perceived risk. Active investments, such as rental properties, wholesaling, and house flipping, are frequently time-consuming, labor-intensive, and require some knowledge to be profitable.
Passive real estate investors supply merely the funds and allow specialists to invest in real estate on their behalf, typically through a fund. Passive investors have less obligation and have more access to numerous types and quantities of investments. For example, REITs, mutual funds, and real estate investment platforms are often low-effort and hands-off, requiring no knowledge.
Real estate is an excellent investment. It can provide continual passive income and be a wise long-term investment if its value rises with time.
Still, you must ensure that you are prepared to invest in real estate. You may not need to invest a lot of money upfront if you are passively investing. Some funds will permit you to invest $1000. On the other hand, you probably will need to invest lots of money upfront if you are actively investing. Purchasing a home, an apartment complex, or a plot of land can be costly. Not to mention the costs you’ll be liable for and the possibility of income gaps if you’re between tenants for an extended period.
******************************
Come join us! Email me at mark@dolphinpi.us to find out more about our next real estate investment.